Almost one out of every four cases of stroke in the United States each year is due to Carotid Artery Disease.
What is Carotid Artery Disease?
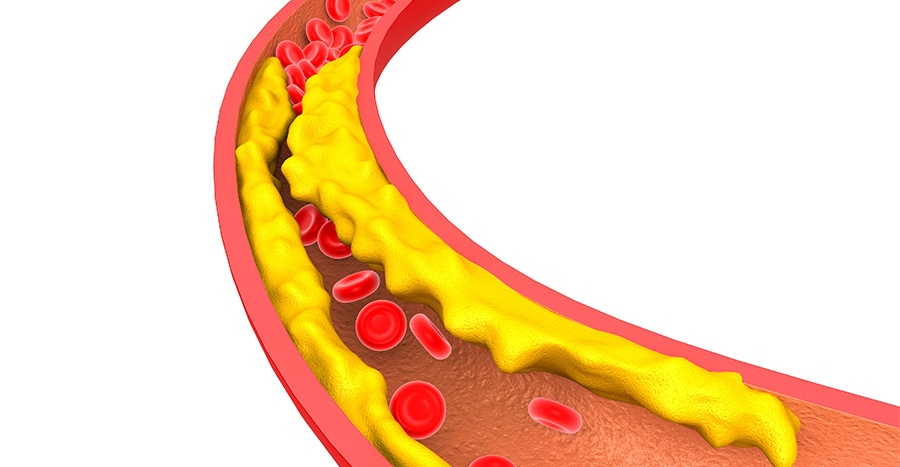
The carotid artery is a pair of arteries that are located at the front of our neck and carry oxygenated blood to the large front part of the brain. Carotid artery disease is a condition in which one or both of these arteries become narrow (stenosis), ulcerated, or completely occluded due to an accumulation of fibrous and fatty material called plaque (atherosclerosis). It restricts the supply of blood to the brain.
What are the Effects of Carotid Artery Disease?
Carotid artery disease significantly increases the risk of Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) or stroke.
How CAD Increase the Risk of Stroke?
CAD occurs due to an accumulation of plaque in the arteries. This plaque can fragment and travel (embolus) to the brain resulting in obstructed blood flow and hence a stroke may occur anytime.
Stroke is of Three Types:
- Ischemic stroke: It is a stroke that is caused by blockage due to a blood clot in a blood vessel in the brain.
- Hemorrhagic stroke: The bursting of blood vessels causes bleeding inside the brain.
- “Mini-strokes” or transient ischemic attacks (TIAs): It occurs when the blood supply to the brain is briefly interrupted.
How would I know if I have a CAD or TIA or Stroke?
Carotid artery disease may or may not cause any symptoms in the person. In symptomatic cases, a person complains of angina or chest pain. In many cases, CAD remains asymptomatic and is diagnosed after the person has a stroke or a transient ischaemic attack (TIA).
The signs and symptoms of TIA and STROKE are almost the same and can only be distinguished by duration and imaging. The imaging studies in TIA are negative while stroke is usually associated with positive imaging results. The symptoms last less than 24 hours in TIA but last longer than 24 hours in stroke. The patient may complain of:
- Loss of vision in only one eye
- Numbness, weakness, or paralysis of one side of the body or face
- Problems with balance or coordination
- Trouble speaking or understanding speech
- Confusion and dizziness
- Severe headache without any cause
Why Is Immediate Treatment Necessary in Stroke?
Stroke can cause temporary or permanent disabilities depending upon the length and part of the brain affected by disruption of blood supply to the brain. It may cause complications like:
- Paralysis or loss of muscle movement
- Difficulty talking or swallowing
- Memory loss or thinking difficulties
- Depression
- Pain, numbness, or other strange sensations in body parts
Treatment for Stroke:
Treatment depends on the type of stroke.
Ischemic stroke: Emergency treatment is done with clot-busting drugs like Aspirin or IV injections of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (TPA). Sometimes emergency procedures like Intra-arterial thrombolysis (delivering medication directly to the brain) or Mechanical Thrombectomy (using a device to break up or remove clots) are performed as soon as possible. Additionally, one of the following procedures may be required to prevent a stroke in the future:
- Carotid endarterectomy
- Angioplasty and stents
Hemorrhagic stroke: Emergency treatment is done to control bleeding, reduce pressure in the brain, lower blood pressure and prevent vasospasm or seizures. Sometimes one of the following surgeries may be required after a stroke if it’s been caused by an aneurysm or arteriovenous malformation (AVM) or other type of vascular malformation:
- Surgical clipping
- Coiling (endovascular embolization)
- Surgical AVM removal
- Intracranial bypass
- Stereotactic radio surgery
For an early diagnosis of Carotid Artery related complications, make an appointment to get yourself diagnosed at Dr. Shaheen’s clinic. Don’t hesitate to contact us.